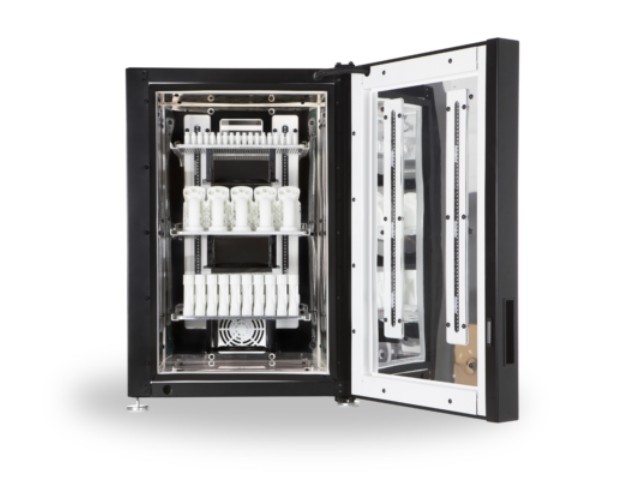
3D printers
High quality 3D printers

Resin printers make parts from liquid resin that hardens under UV light. Resin printers build parts in layers, similar to filament printers, but they do so by exposing each layer to a pattern of UV light to solidify the resin where it is needed. DLP (Digital Light Processing) and SLA (Stereolithography) are two typical types of resin printers you will see. Some of the newer types of resin printers are from Nexa3D®, which uses LSPc® (Lubricant Sublayer Photo-curing) technology, and Inkbit Vista™, which uses VCJ (Vision-Controlled Jetting) technology.
The light source used in DLP is UV light from a projector, and the UV light source remains stationary while curing the entire resin layer at once. With DLP 3D printers, the operator can usually control the intensity of the UV light source and thus its effect on the resin.
The light source used in SLA is a UV laser beam that moves from point to point and traces the geometry. With SLA, the intensity of the laser beam usually cannot be adjusted, so you have to change the laser light completely for different plastic effects.
LSPc® technology starts with a uniform light source. Using a UV light array and a high contrast mask responsible for projecting the 3D slices onto the tray where the photopolymerization process takes place layer by layer, a uniform, distortion-free image is created in all areas of the build plate, ensuring part-to-part uniformity and accuracy.
With advanced inkjet technology that applies the resin layer by layer and Vison-Controlled Jetting (VCJ) technology that creates a topographic map of each layer after application, the scan data from each layer is used in conjunction with the geometry of the initial part to create the next layer. Real-time dynamic layer generation ensures that parts are produced quickly and accurately every time.
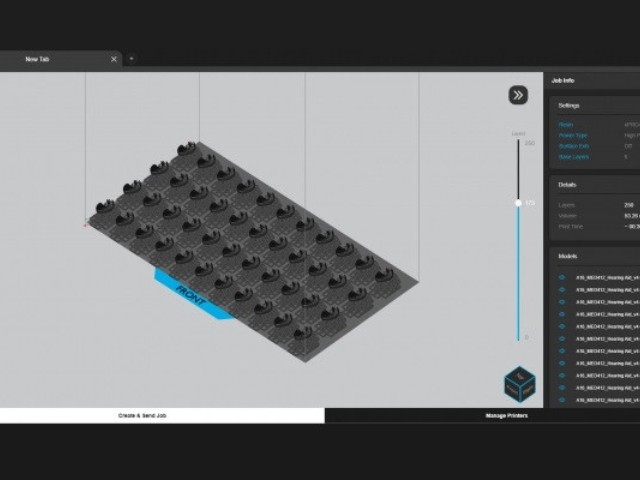
The first step involves preparing the print data with a selected CAD or 3D printer software. Subsequently, the prepared data is transferred to the 3D printer and processed.
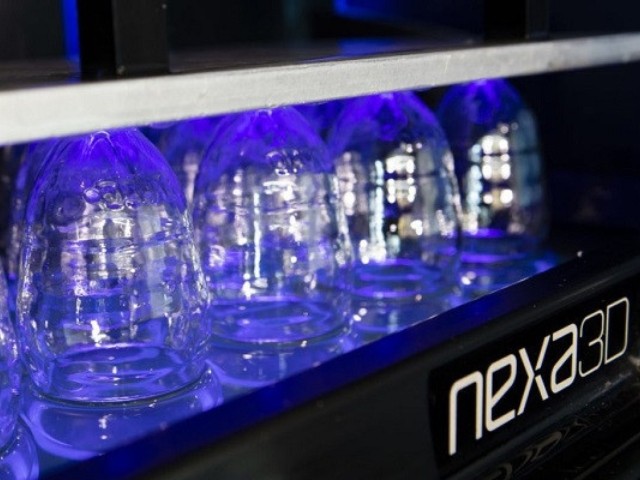

After a brief check of the correct print settings, the printing process begins and the 3D printer can run unattended until completion. For printers with cartridge system, the refilling of material is fully automated.
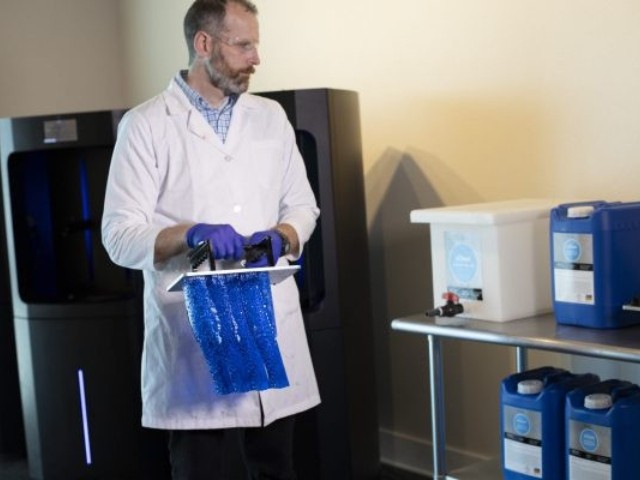

Once the printing process is complete, the component can be removed from the build chamber. Depending on the geometry, the components are now removed from the build platform. Frequently, however, the components also remain on the build plate until they have been washed and hardened.
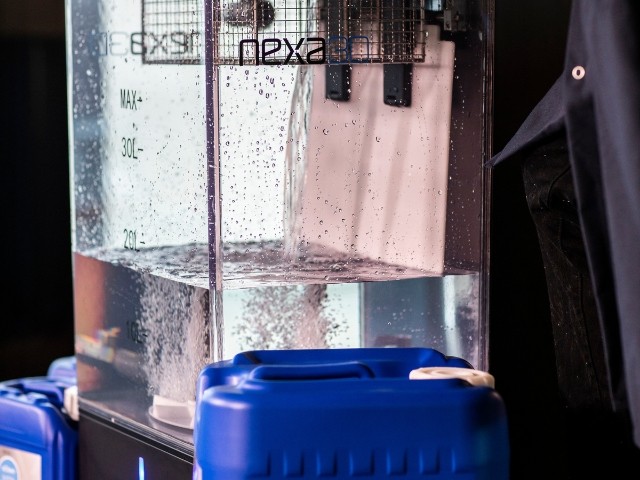

The components are then briefly washed in a solvent. In this step, the excess resin is removed from the surface.

The materials do not reach the maximum degree of polymerization due to the pressure. Therefore, the components are post-cured after washing. Hardening takes place in a UV oven to achieve the highest possible strength and stability.
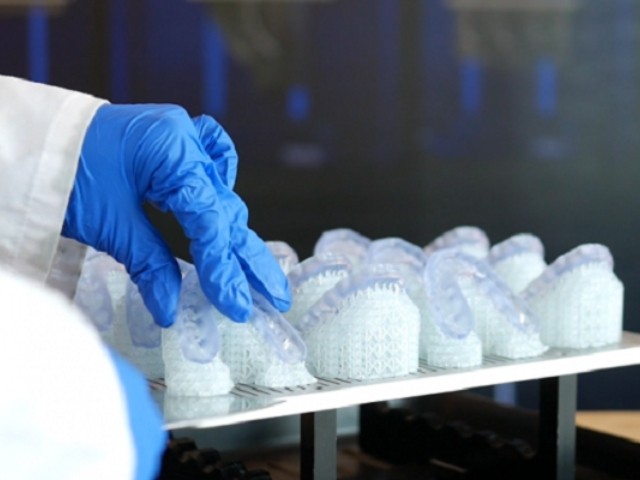

In the final step, the support structures are removed. Here, the component can also be mechanically reworked. The parts can be painted very well.
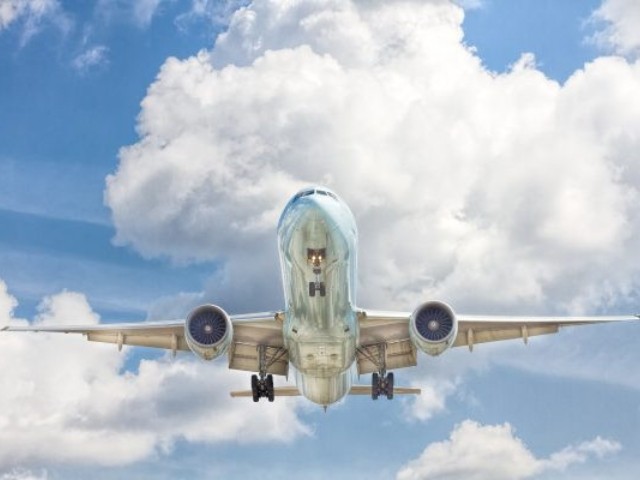

Resin-printed components are lightweight with good mechanical properties - even with temperature fluctuations. Due to the stability and wear resistance, resin prints are popular in the aerospace industry.
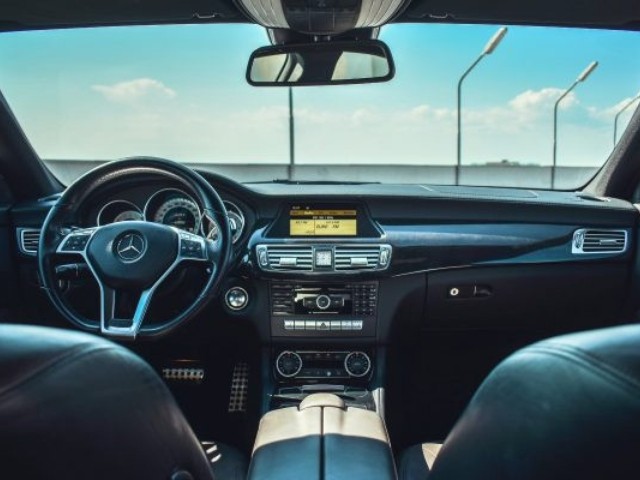

The lightweight and resilient materials can save weight and promotes lower fuel consumption in the automotive industry. The application of resin 3D printing processes are therefore widely used.

In the sports and leisure segment, resin components are used for the construction and repair of boats, sailors and boards. Manufacturers from the sports shoe sector are also increasingly working with resin-based 3D printers.
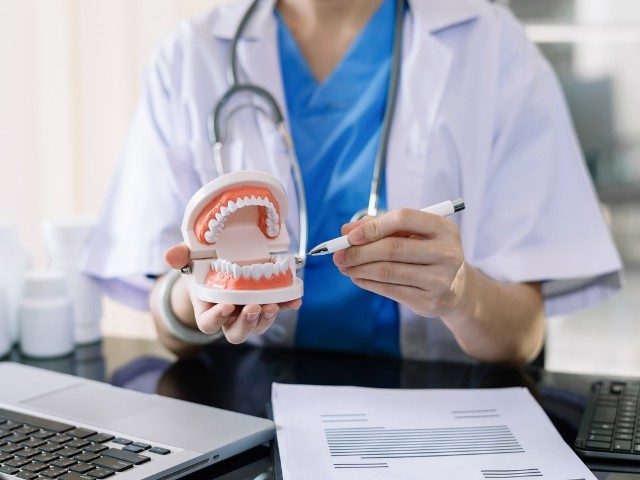
Dental acrylics enable dental laboratories and practice labs to rapidly fabricate biocompatible surgical guides, splints, fixed guides, models and full dentures.

Resin 3D printing in the medical industry can be used to print organ models and usable casts and splints. These could also be helpful in patient education and preoperative planning for surgeons.

Integrate Resin 3D printed rapid tooling into your design process to accelerate product development, iterate faster and bring better products to market. Before you move to mass production, you can use rapid tooling to confirm your design and material selection.
Our team of experts will be happy to support you in choosing the right 3D printing technology and in selecting the right 3D printing system.
Our application team also advises you on the choice of materials. Among other things, we can provide cost and time calculations as well as sample parts. In our showroom we have the possibility to validate the project together with you!
