What does the defense sector refer to?
The defense sector includes government and commercial firms and companies that research, develop, engineer, manufacture, and service military equipment, materials, and technologies. It is an important and distinguishing aspect of the modern economy. The defense sector includes a wide range of products and services in addition to weapons manufacturing, such as military healthcare, maintenance, logistics, and information technology support. It is a key employer, with thousands of small and medium-sized firms providing specialised skills, equipment, and services to strengthen national security and defense capabilities.
What are the divisions within the defense sector?

Military Divisions
The defense sector is made up of many military divisions that specialize in particular operational capabilities and roles. The Army, for example, is divided into infantry, armored, mechanized, air defense, strategic, and artillery units. The Air Force has divisions for fighters, bombers, airlift, air defense, and space. The Navy has surface, submarine, aviation, and amphibious divisions. The Marine Corps also has its own specialist divisions. These military divisions are normally brigade-sized organizations of between 3,000 to 5,000 soldiers, led by a colonel. They are the primary tactical units capable of conducting independent operations and supporting battlefield missions. Higher-level organizational levels, such as corps and field armies, give operational guidance and coordination to these military divisions.

Functional Divisions
The defense sector also includes a number of functional divisions that support the military's overall capabilities and activities. These include divisions dedicated to equipment maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO), prototyping and research and development, gear and system customization and personalization, lightweight and complex structure production, unmanned systems and robotics development, and supply chain and logistics management. These functional divisions use specialized skills, technologies, and processes to improve the military's preparedness, performance, and response. They collaborate closely with military divisions to enable timely delivery of vital capabilities and solutions. The defense sector's organizational structure contains both military and functional divisions to fulfill the many needs of national defense.
What are the organizational departments and agencies that make up the defense sector in Europe?

European Defense Agency (EDA)
The European defense Agency (EDA) is an intergovernmental agency of the European Union that promotes and strengthens European defense cooperation in support of the EU's Common Security and defense Policy. It collaborates with EU member states to develop European defense capabilities through joint defense programs and activities.

NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
NATO, as a military alliance, coordinates European member nations' defense efforts, including cooperative exercises, operations, and capabilities development. NATO has various commands and agencies that help it achieve its military and security objectives, including Allied Command Operations and Allied Command Transformation.

Each European country has its own ministry of defense, which is responsible for the armed forces and military strategies. Examples of this are the Dutch Ministry of Defense and the armed forces of the Royal Netherlands Army.

EU Defense Industrial and Technological Base
The European Union is trying to boost its defense industrial and technology basis through programs such as the European defense Industrial Programme (EDIP) and the European defense Fund. This includes coordinating defense procurement, promoting defense research and development, and increasing the competitiveness of the European defense industry.

Other European Defense-Related Agencies and Organizations
a. European Union Military Staff (EUMS): The directorate-general of the European Union's External Action Service that contributes to the EU's Common Security and defense Policy (CSDP). It provides military expertise and support, including early warning, situation assessment, strategic planning, and the coordination of CSDP operations and missions.
b. European Union Satellite Centre (SatCen): An agency of the European Union that provides geospatial intelligence support to the EU's Common Foreign and Security Policy, including the Common Security and defense Policy.
c. European Union Institute for Security Studies (EUISS): The Union's agency dealing with the analysis of foreign, security and defense policy issues.
What are the benefits of 3D printing in the defense sector?
Rapid Prototyping and Design Validation
3D printing enables defense engineers to rapidly iterate on designs, evaluate form and function, and make educated judgments early in the development process. This shortens development time and assures that finished goods fulfill exacting criteria.
Customization for Mission Success
3D printing enables the defense industry to develop custom components and equipment that are suited to specific mission requirements, ranging from personalized soldier gear to specialist vehicle and aircraft parts. This ensures precision and efficiency in production.
On-Demand Spare Parts Production
3D printing allows for on-demand fabrication of replacement parts, minimizing the need for large stocks and ensuring important equipment can be fixed or replaced promptly in the field, even in remote places. This improves operational readiness.
Complex Geometry and Lightweight Structures
3D printing enables the fabrication of detailed, lightweight structures that enhance the performance and efficiency of military equipment and systems, such as airplanes, vehicles, and other defense platforms.
Supply Chain Resilience
3D printing decreases reliance on traditional supply networks, allowing the defense industry to manufacture parts on demand while also mitigating supply chain weaknesses.
Intellectual Property Rights for In-house 3D Printing
To prevent external counterfeiting, information leaks, and internal misuse of 3D printed parts, access to data on accompanying CAD/STL files, as well as the number of allowed printings or applications can be controlled and localised to safeguard intellectual property rights.
What are the applications of 3D printing in the defense sector?
Spare Parts
The defense sector is using 3D printing to manufacture a wide range of crucial spare parts and replacement components on demand. This comprises vehicle and aircraft elements such as tank track links and protective housings for equipment, as well as weapons and munitions components, 3D printed medical devices and supplies like custom Epi-Pen carrying cases, stethoscopes, IV line controls, tracheal tubes, splints, casts, COVID-19 swabs, and face shields and even 3D printed multi-tools, jigs, and other specialized tools that can be quickly created and used by military personnel.
Customized Gear and Equipment
The defense sector can use 3D printing to make unique, tailored gear and equipment for soldiers, such as specialized impact absorption and protective armor suits, combat helmets, accessories, and other mission-specific goods. It can be used to create weapons, firearms, customizable grips, sights, and other firearm attachments that are specific to the user's tastes and ergonomic requirements. Furthermore, 3D printing allows the creation of specialized tools, equipment, and gear that may be tailored to the specific needs of various military roles and operating environments.
Prototypes and Simulation Models
Engineers can use 3D printing to swiftly create concept models and functional prototypes without the need for additional tooling, resulting in faster design iteration and validation. This is especially useful in speeding the development of new military equipment, weapons, and systems. Beyond prototypes, 3D printing enables the creation of realistic training aids and simulation models, which can improve soldier readiness and mission rehearsals. For example, 3D printed prototypes of new cockpit layouts help pilots to become acquainted with the designs more quickly than traditional methods.
Unmanned Systems and Robotics Components
3D printing is essential for the rapid development and production of important components for unmanned systems, drones, and military robotics in the defense sector. For example, 3D printing can be used to create unique housings, mounts, and structural components for small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and ground-based robotic systems. This competence allows the military industry to rapidly manufacture and deploy new technologies, which are becoming increasingly critical for surveillance, reconnaissance, and other specialized operations.
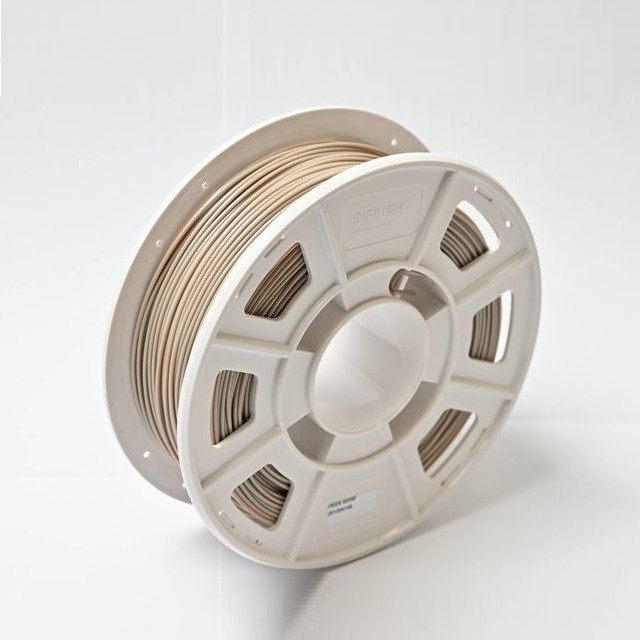
What materials do we recommend for 3D printing in the defense sector?
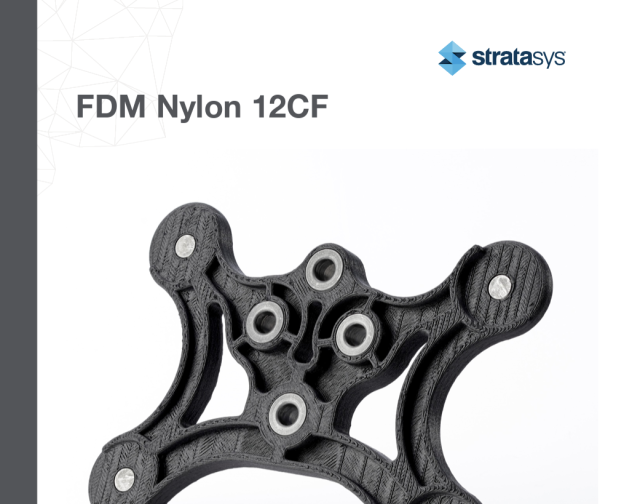
FDM Nylon 12CF (Carbon Fiber) from Stratasys® - Printed on the Stratasys® F900™
FDM Nylon 12 Carbon Fiber (Nylon 12CF) is a remarkable material that combines the strength and stiffness of Nylon 12 with the benefits of chopped carbon fiber. This unique blend achieves the highest flexural strength and stiffness-to-weight ratio among all FDM materials, making it a highly versatile and valuable additive manufacturing solution.
In many applications, the exceptional strength and stiffness of Nylon 12CF are sufficient to replace heavy metal components. This allows manufacturers to create lighter, more ergonomic tools and functional prototypes that can significantly improve productivity and efficiency. By leveraging the power of carbon fiber FDM, companies can validate designs faster and more cost-effectively than traditional metal prototyping methods.
The F900™ is the ideal platform for leveraging the capabilities of Nylon 12CF. This proven 3D printing system delivers precise, dependable performance, enabling manufacturers to speed up their production processes and reduce costs. With its reliable performance and the ability to utilize the high-performance Nylon 12CF material, the F900™ has become a trusted solution for manufacturers in the defense industry and beyond.

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
ULTEM™ 9085 from Stratasys® - Printed on the Stratasys® F900™
ULTEM™ 9085 is a remarkable high-performance thermoplastic filament that offers exceptional physical and mechanical properties, making it an ideal choice for demanding and specialized applications utilizing FDM technology. As one of the strongest Stratasys® FDM materials, ULTEM™ 9085 boasts an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a prime candidate for high-strength, low-weight applications.
In addition to its impressive strength, ULTEM™ 9085 filament also exhibits outstanding impact resistance and excellent chemical tolerance. Crucially, it meets the stringent transportation industry standards for flame, smoke, and toxicity, further expanding its versatility and suitability for a wide range of mission-critical applications.
The F900™ is the ideal platform for leveraging the capabilities of ULTEM™ 9085. This proven 3D printing system delivers precise, dependable performance, enabling manufacturers to revolutionize their supply chains, accelerate production, and reduce costs. With its reliable performance and the ability to utilize the high-performance ULTEM™ 9085 material, the F900™ has become a trusted solution for manufacturers in the defense sector and beyond.

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
ULTEM™ 1010 resin from Stratasys® - Printed on the Stratasys® F900™
ULTEM™ 1010 resin is a remarkable 3D printing material that boasts exceptional durability and performance. Crafted from high-performance polyetherimide (PEI) thermoplastic, this substance offers unparalleled heat resistance and the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion among all FDM materials.
With its exceptional strength qualities, ULTEM™ 1010 resin stands out as the strongest FDM material available, making it an ideal choice for demanding and specialized applications. This includes the production of lightweight composite tools, where its high-performance characteristics are truly put to the test.
The F900™ is the ideal 3D printing system for leveraging the exceptional properties of ULTEM™ 1010 resin. This proven platform delivers precise, dependable performance, enabling manufacturers to save on production costs and streamline their additive manufacturing processes. With its reliable performance and the ability to utilize the high-performance ULTEM™ 1010 material, the F900™ has become a trusted solution for manufacturers in the defense sector.

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
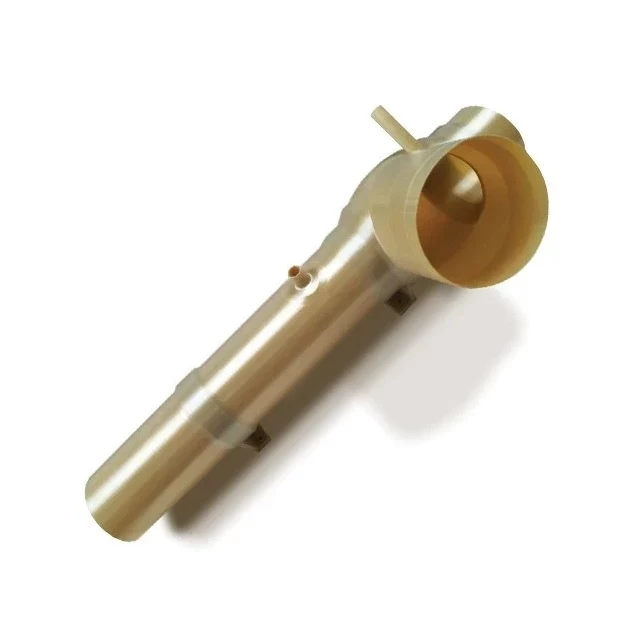
INFINAM® PEEK from Evonik - Printed on the Roboze ARGO 500
One of the standout features of the INFINAM® PEEK filament is its exceptional temperature resistance, making it an ideal choice for printing components that must withstand extreme environmental conditions. This remarkable material boasts a glass transition temperature of 152°C, allowing it to endure long-term temperatures of up to 250°C and short-term temperatures of up to 300°C. This capability enables the fabrication of parts that can be reliably used in the most hostile environments.
In addition to its impressive thermal properties, INFINAM® PEEK filament is also exceptionally resistant to a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds. This material only dissolves in intense sulfuric and nitric acid, further expanding its versatility and suitability for demanding applications.
To fully harness the capabilities of INFINAM® PEEK, the Roboze ARGO 500 is a high-temperature industrial 3D printer that has been specifically designed to work with this material. Manufactured by the Italian company Roboze, the ARGO 500 features an extruder capable of reaching temperatures up to 450°C and a build envelope that can heat up to 180°C. This advanced system is compatible with the INFINAM® PEEK filament from Evonik, enabling the creation of large-format parts with a positioning accuracy of 10 µm and consistent repeatability.
ARGO 500

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
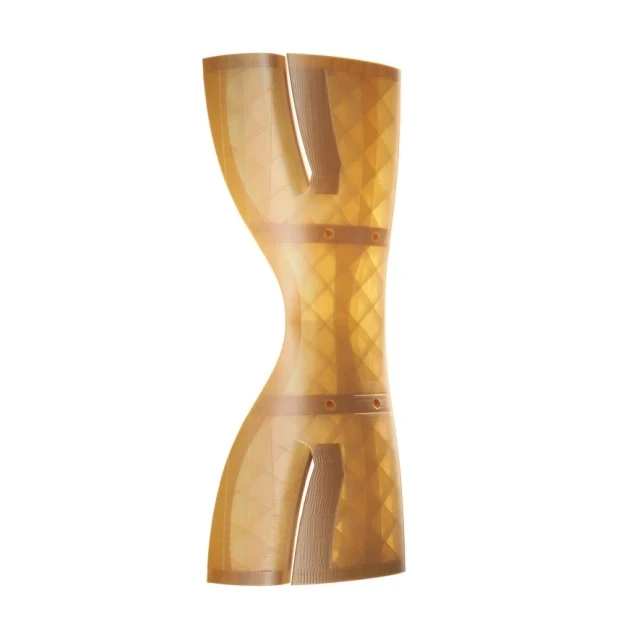
Somos® PerFORM™ from Stratasys® - Printed on the Stratasys® Neo®800
Somos® PerFORM™ is the resin of choice for composite parts that demand exceptional strength, stiffness, and resistance to high temperatures. This remarkable material is suitable for a wide range of applications, including tooling, wind tunnel testing, high-temperature testing, electrical casings, and automotive housings, thanks to its superior heat tolerance, detail resolution, and overall stiffness.
One of the standout features of Somos® PerFORM™ is its low viscosity, which is the lowest among all composite stereolithography materials. This property allows for faster build times, easier post-processing, and superior sidewall quality, resulting in unrivaled detail resolution. Somos® PerFORM™ is a ceramic-based material that boasts extremely high heat tolerance and rigidity, further enhancing its performance capabilities.
To fully leverage the potential of Somos® PerFORM™, the Stratasys® Neo®800 has been designed with the customer in mind, delivering reliable, gold-standard SLA 3D printing. When using this advanced system with the Somos® PerFORM™ resin, manufacturers can produce dimensionally accurate parts with exceptional sidewall quality and crisp feature resolution, leading to a 50% reduction in finishing time.

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
xESD resin from Nexa3D® - Printed on the Nexa3D® XiP Pro
The Nexa3D® family of functional materials includes the stiff, black xESD resin, which boasts exceptional static-dissipative qualities. This remarkable material is formulated with discrete carbon nanotubes that are evenly distributed atop a robust urethane dimethacrylate foundation.
The inclusion of carbon in the xESD resin not only provides superior electrostatic dissipative performance but also results in parts with greater tensile strength, a higher tensile modulus, and increased impact resistance. Additionally, the carbon-infused resin ensures a mark-free surface finish, further enhancing the overall quality and appearance of the printed components.
To fully harness the capabilities of the xESD resin, Nexa3D® has developed the XiP Pro, an ultra-fast resin 3D printer specifically designed for this material. Leveraging the company's unique LSPc® technology, the XiP Pro enables the rapid manufacture of ESD-resistant parts with high resolution in a matter of hours, revolutionizing the additive manufacturing process.
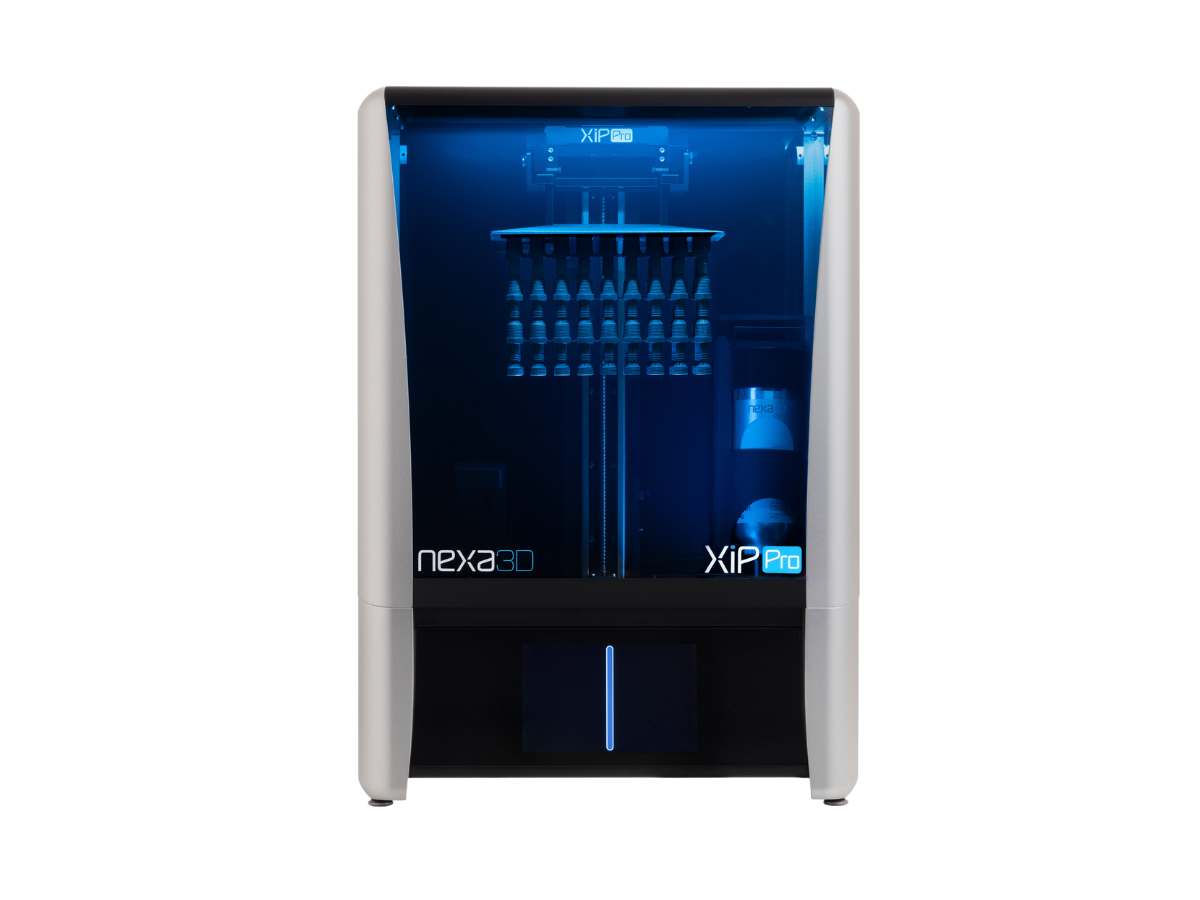

XiP Pro
















