What does ESD stand for?
A sudden and momentary electric current flow between two objects at differing electrical potentials is known as an electrostatic discharge (ESD), and it is usually the result of accumulated static charge being released. This phenomena can happen when two insulators come into contact, split apart, and the potential difference between them ignites as an arc or spark. ESD is a crucial factor to take into account in sectors including electronics manufacturing, aircraft, and healthcare since it presents a serious risk to delicate electronic components, possibly leading to damage or malfunction.
What are the ESD protection classes?
Human Sensitivity
Discharges of static electricity can be felt by humans at voltages as low as 3,000 volts. On the other hand, damage to electrical components can happen at voltages far lower than what is often felt by humans.

ESD Threshold for Electronic Components
At ESD levels of 100 volts or less, a lot of electronic components are vulnerable to damage. Even at discharge voltages of 20–30 volts, integrated circuits (ICs) and other semiconductor devices can sustain irreversible damage.
What are the costs connected to ESD damages?
Industry Impact
The electronics sector is predicted to lose billions of dollars a year due to damage caused by ESD. ESD-related failures can happen during any phase of production, assembly, testing, or even transit.
Product Liability
The cost of ESD-related failures goes beyond monetary losses in industries where dependable electronic components are essential, such as aerospace and medical devices. Recalls of products, harm to one's reputation, and even legal repercussions are possible outcomes.
What are the benefits of 3D printing for ESD applications?
Customization
Using 3D printing, highly tailored ESD-safe components can be made. Manufacturers can create complex shapes that are customized to meet individual needs and guarantee the best possible ESD protection. It is difficult to attain this degree of personalization using conventional production techniques.
Rapid Prototyping
3D printing makes it possible to swiftly create ESD-safe prototypes, facilitating more rapid design revisions and advancements. This shortens the time it takes for ESD-sensitive devices to go on sale by speeding up the product development cycle.
Complex Structures
Conventional manufacturing methods frequently have trouble creating the complex and complicated structures needed for ESD applications. These difficult geometries are wonderfully created by 3D printing, which offers an excellent way to safeguard complex electronic components from ESD.
What are the applications of 3D printing in ESD-sensitive industries?
Electronic Components
Electronic components such as connections and housings that are ESD-safe are made utilizing 3D printing. ESD-compliant materials allow for the creation of complex designs that guarantee the best possible protection for delicate electronic equipment.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace uses 3D printing to create lightweight, ESD-safe components because ESD protection is essential for avionics and electrical systems. This helps keep the aircraft's total weight down while upholding the essential safety requirements.
Medical Devices
By creating ESD-safe enclosures for delicate medical equipment, 3D printing helps the medical sector. This complies with strict ESD regulations and guarantees the dependable operation of electronic equipment in healthcare environments.
What materials do we recommend for ESD-compliant 3D printing?
xESD resin from Nexa3D® - Printed on the Nexa3D® XiP Pro
The stiff, black xESD resin from the Nexa3D® family of functional materials has static-dissipative qualities. The discrete carbon nanotubes in the xESD resin are equally placed atop a stiff urethane dimethacrylate foundation.
The inclusion of carbon in the xESD results in parts that are free of markings and, in addition to their isotropic electrostatic discharge capacity, have a higher tensile strength, a higher tensile modulus and very good temperature resistance.
The XiP Pro printer from Nexa3D® is one of the ultra-fast resin 3D printers that are specifically made for the xESD resin. The unique LSPc® technology of Nexa3D® allows for the rapid manufacture of conductive parts with high resolution in a matter of hours.
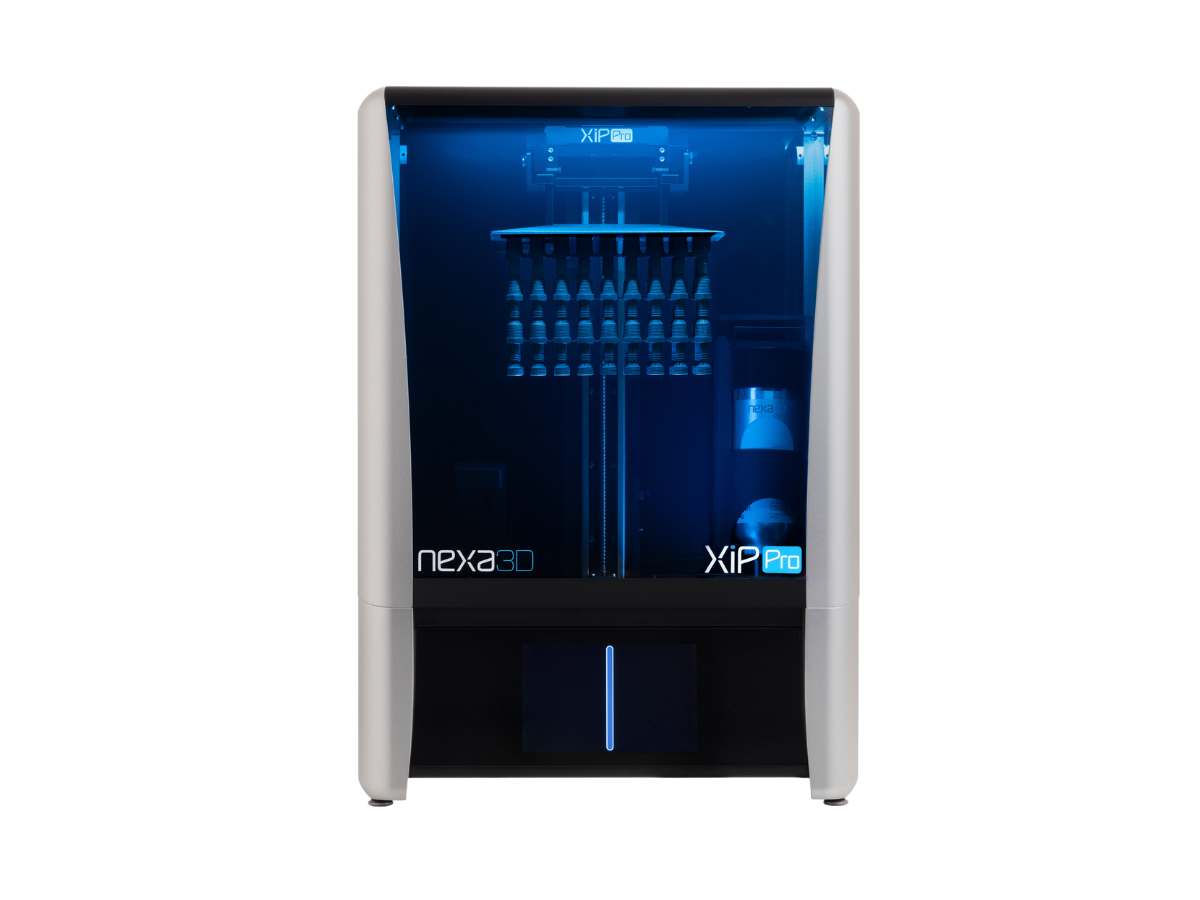

XiP Pro

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
ABS-ESD7 filament from Stratasys® - Printed on the Stratasys® F370
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Electrostatic Dissipative, or ABS-ESD7, is an ABS thermoplastic having the ability to dissipate static electricity. It stops static energy from building up, preventing discharges and drawing in other things like dust, powder, and small particles.
The FDM material ABS-ESD7 is a filament that dissipates electrostatic charges (ESD) by fusing carbon fiber (carbon) with the strength and durability of ABS. Using ESD-ready ABS material, it is used to print prototypes, electronics supports and fixtures, and other electrostatically sensitive applications.
Stratasys®'s industrial FDM 3D printers, such as the F370 from the F123CR Composite Ready Series, which provides high-strength carbon fiber materials on a dependable, user-friendly industrial printer platform, are specifically made for printing the ABS-ESD7 filament.

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
Antero 840CN03 from Stratasys® - Printed on the Stratasys® Fortus® 450mc
Antero 840CN03 is a PEKK-based and electrostatically dissipative high-performance thermoplastic (ESD) that provides unparalleled strength, heat and chemical resistance, resilience, and a lightweight metal alternative.
The Antero 840CN03 FDM high-performance fiber allows you to create highly tailored parts with constant qualities for static dissipation, chemical resistance, and extremely low outgassing.
The Fortus® 450mc is suitable for applications that require precise prototypes, strong manufacturing tools, or on-demand finished components.The Fortus® 450mc is an additive manufacturing multi-tool designed to print the Antero 840CN03 filament to create soft jaws and electrostatic discharge-resistant components.

Have your components 3D printed now! Do you have any questions? Contact our experts!
TPU-ESD filament from 3DXTECH - Printed on the Roboze ARGO 350
The engineering-grade thermoplastic 3DXSTAT™ ESD-Flex TPU [90A] [thermoplastic polyurethane] elastomer was selected for its high flexibility, ease of printing, chemical resistance, and durability. The goal surface resistance of 3DXSTAT™ ESD Flex elastomeric filament is 10³ Ohm, and it is designed to provide ESD-Safe electrical conductivity.
Because of the filament's strong elongation of over 300%, shore 90A semi-flex hardness, minimal moisture absorption that maintains flexibility even at low temperatures, jigs, casings, conveying, metering, and sensing applications are typical ESD uses of this filament.
The ARGO 350 from the Italian manufacturer Roboze prints this material with outstanding qualities. The industrial printer lets you produce your parts in a matter of hours. Create large-format finished parts with a 3D printer with 10 µm positioning accuracy and consistent repeatability.

ARGO 350






